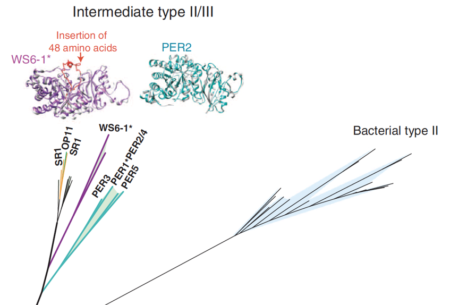
Phylogenetic analyses of the RuBisCO large subunit (portion of tree) and protein models. One Form II/III RuBisCO was selected for functional testing
Scientific Achievement
Metagenomics significantly expanded the diversity of RuBisCO enzymes, revealing examples from CPR bacteria that are inferred to function in the AMP salvage pathway. Catalytic activity was demonstrated.
Significance and Impact
Identification of RubisCOs across a radiation of obligately fermentative, small celled organisms hints at a widespread, simple metabolic platform in which ribose may be a prominent currency.
Research Details
- Genomes were recovered from the subsurface
- Sequences were profiled to identify RuBisCO genes and the proteins analyzed phylogenetically.
- Pathway reconstruction was performed
A form II/III RuBisCO was shown to complement growth in a bacterial photoautotrophic RuBisCO deletion strain
Citation
Wrighton, K. C.; Castelle, C. J.; Varaljay, V. A.; Satagopan, S.; Brown, C. T.; Wilkins, M. J.; Thomas, B. C.; Sharon, I.; Williams, K. H.; Tabita, F. R.; Banfield, J. F. (2016) RubisCO of a nucleoside pathway known from Archaea is found in diverse uncultivated phyla in bacteria, Isme Journal, 10(11), 2702-2714 DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2016.53.