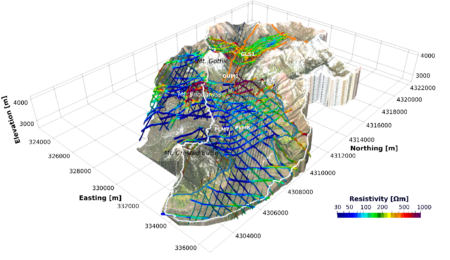
Digital elevation model of the East River Watershed, overlain by an aerial photograph and geophysical data used in this study.
The Science
Because they provide more than half of earth’s freshwater, mountainous watersheds are often referred to as the world’s “water towers”. Climate change can influence watershed function and how they provide water to communities downstream. To predict the impact of this change, scientists must understand how water flows in the ground and how the earth’s properties affect this flow. However, measuring the earth’s properties is difficult – especially over a large area. Researchers have tested how to use observations from space or from the air to estimate the earth’s properties. The team demonstrates this method at a mountainous watershed close to Crested Butte, CO, one of the best characterized watersheds in the world. The team demonstrates that, although the relationships are complex, the earth’s subsurface properties vary with properties on the earth’s surface, such as the angle of hillslopes, their gradient, elevation, and the vegetation that grows on them. Using these relationships, researchers can predict what the subsurface looks like and map features in the subsurface that are controlling groundwater flow.
The Impact
Protecting and monitoring groundwater is becoming increasingly critical in light of climate change and prolonged droughts. Understanding how the subsurface is impacting groundwater flow is crucial to predict how this resource may change over time and to develop management approaches. This research shows that critical subsurface properties can be predicted from observations of the Earth’s surface, which are much easier to measure. Knowing the Earth’s properties will eventually lead to a better management of groundwater resources and drought resilience.
Summary
Bedrock measurements are critical for predicting the hydrological response of watersheds to climate disturbances. However, estimating how water flows in the bedrock over watershed scales is difficult, particularly in areas where bedrock may be cracked. By linking data from subsurface and surface measurements, researchers used machine learning to test the covariability of above and belowground features throughout an entire watershed. The team studied the relationships between bedrock properties, surface formation features, and vegetation to show that relationships derived from machine learning can estimate most of their covariability. Using these relationships, the team predicted the bedrock properties across the watershed and showed that regions of lower variability provide better estimates. The results emphasize that this integrated approach can be used to derive bedrock characteristics on a smaller-scale, allowing for a better understanding of subsurface variations across an entire watershed. Knowing how bedrock may vary with surface properties may be critical to assess the impact of disturbances on freshwater function in these ecosystems.
Citation
Uhlemann, et al., Surface parameters and bedrock properties covary across a mountainous watershed: Insights from machine learning and geophysics. Science Advances 8 (2022). [DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abj2479]